Entrepreneurship Development through Agro-Processing Centers in Production Catchment for Secured Farmers Income by Mohammed Shafiq Alam* in Open Access Journal of Biogeneric Science and Research
Short Communication
An agro-processing industry or centre refers to the subset of manufacturing that processes raw materials and intermediate products derived from the agricultural sector. Agro-processing industry thus means transforming products originating from agriculture, forestry and fisheries. A very large part of agricultural production undergoes some degree of transformation between harvesting and final use. The industries that use agricultural, fishery and forest products as raw materials comprise a very varied group. They range from simple preservation and operations closely related to harvesting to the production, by modern, capital-intensive methods, of such articles as textiles, pulp and paper.
The potential for agro-industrial development in the developing countries is largely linked to the relative abundance of agricultural raw materials and low-cost labour in most of them. The most suitable industries in such conditions make relatively intensive use of these abundant raw materials and unskilled labour and relatively less intensive use of presumably scarce capital and skilled labour.
At present, farming alone no more seems to be a viable and remunerative venture for small and medium farmers, unless properly espoused with value addition through efficient primary processing operations carried out, in the production catchments itself, by the farmers transformed into processors. Rural entrepreneurship through suitable agro-processing models/complexes is essential to increase the income of the farmers, provide significant employment opportunities to the rural youth and reduce huge amount of post harvest losses especially in cereals, spices, cotton and oil-seeds. Based on the resource availability in an agro-climatic zone, agro-processing models for various regions of Punjab were developed and validated in a research Project in AICRP on Post Harvest Engineering & Technology.
The concept of Agro Processing Centres (APCs) was to process the grains at the village level to substantially enhance the income of the farmers. Moreover, the primary processed products from wheat, paddy, oilseeds, pulses etc are of daily use in every household. So there lies a great potential for the primary processing of these durable food grains. These agro processing complexes have been found to be technically feasible, economically viable and socially acceptable models. These farmers who have established these complexes have earned to such an extent that they have given up farming and associated their family members in the processing activity. These complexes consist of two or more machines for processing at farm/village level. The machines are mini rice mill, baby oil expeller, small atta chakkies and large atta chakkies with scouring machine, masala grinder, penja, cleaner and feed mill along with construction and installation costing approximate Rs. 20-25 lakhs.
A desired covered space of approx. 200-300 sq.yard is required for the installation of all these machines. Presently more than 300 of such APCs have been installed by the farmers/rural youth under the guidance of PAU directly/indirectly and are being running successfully in different parts of state. The state has a lot of potential for installing similar units all over Punjab. Presently 15-35% subsidy on machinery based on categories is provided by KVIC.
The following advantages have been experienced through APC’s in rural areas:
- Employment generation in the production catchments
- Migration check of unemployed rural youth to urban areas
- Processing of farm product locally
- Increased farm income
- Reduced transportation costs of raw materials/products
- Adulteration free product
- Ease of disposal of waste
- Minimizes pollution from agro-processing in cities
The following agro industrial models have been developed which may be adopted in specific areas depending upon the crop produce of the area:
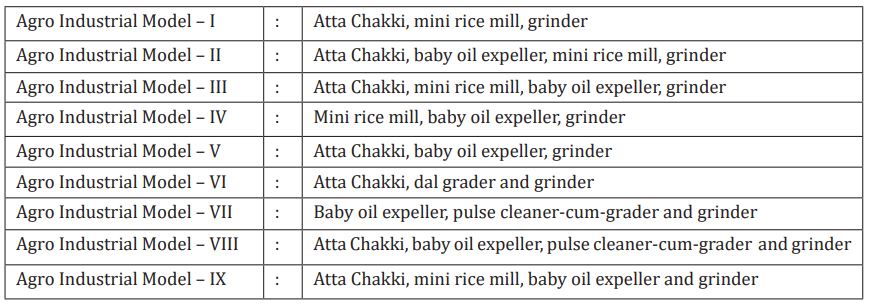
These models consist of two or more machines for processing at farm/village level. A number of such complexes have been adopted by the farmer/entrepreneurs at various places in Punjab. These are technically feasible and economically viable units. Details of agro processing machinery along with their cost are given in Table 1. After deciding the technologies, the components of agro industrial complex can be finalized and a specific agro industrial model can be finally selected for installation.
Table 1: Agro Processing Machinery

a. Extra Cost of Rs 6, 00,000 (for construction of APC shed along with installation of machinery)
b. Cost of packaging material = Rs. 150/- to Rs. 275/- per kg (depending upon the thickness), Printing Charges = Rs. 0.50/package
Selection of suitable agro industrial technology/equipment
For selecting a suitable agro industrial technology/equipment in rural areas, the following important points should be given due consideration:
- Crop production & pattern i.e. availability of raw material
- Technology/process to be used for processing
- Volume of production
- Identification of suitable technologies, plant and machinery for desired volume of production.
- Facility for storage and marketing
Apart from proper selection of equipment, assessment of availability of raw material and market potential, it is also necessary to exercise the following steps:
- Collect benchmark information of selected village and cluster of villages on crops grown, processing of farm produce, and the demand for processed products;
- Identify corresponding post-harvest equipments/technologies based on crops production scenario of cluster and study their techno-economic feasibility;
- Complete formalities for creating infrastructural facilities;
- Get license from appropriate authorities of the government to take up processing activities.
- Install processing equipment and introduce process technologies in APC;
- Constitute a local governing committee to oversee safety and maintenance of agro-processing centre;
- Periodically observe the functional performance and monitor processing machines;
- Develop modalities for credit assistance from banks to procure additional processing equipment as and when needed;
- Develop strategies to include such processing activities/strategies to enable the APC to run for more than nine months in a year;
- Involve Self-Help Groups of Women in the value-added activities as well as marketing of processed products; and
- Obtain technical advice from the competent source to update and keep pace with the changing environment in value-addition activities.
APCs can generate a platform to process the raw produce with ensured good quality finished product and are technically feasible and economically viable units. The entrepreneurs who had already installed the APC with our guidance, running it successfully and are fetching good financial capital with monthly profit of approx. Rs 0.50 to 1.00 lakhs apart from providing employment to 2-5 persons. The state has a lot of potential for installing similar units all over Punjab.
More information regarding this Article visit: OAJBGSR
https://biogenericpublishers.com/pdf/JBGSR.MS.ID.00240.pdf
https://biogenericpublishers.com/jbgsr-ms-id-00240-text/

No comments:
Post a Comment